// JavaProject InputDialog
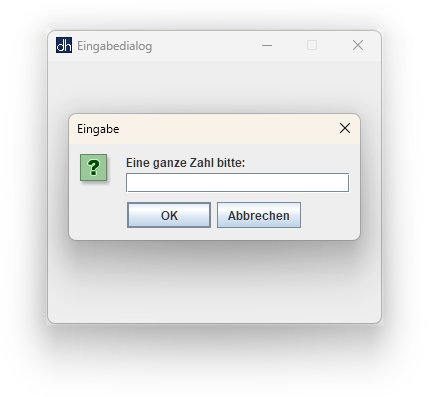
Zwei Eingabedialoge verlangen bestimmte Benutzereingaben. Passt
eine Eingabe nach dem Klick auf den OK-Button nicht zur
gestellten Frage, so wird die Eingabe mit einer Fehlermeldung quittiert und
der Eingabedialog wird wiederholt.
Die Dialogfenster werden erzeugt durch Aufruf der statischen Methoden showInputDialog bzw. showMessageDialog der Klasse JOptionPane. Die Methode showQuestionDialog liefert die jeweilige Benutzereingabe als Zeichenkette zurück. Der Inhalt der Zeichenkette wird anschließend auf Korrektheit überprüft.
// InputDialog.java
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class InputDialog {
Image icon; //
Variablen
JFrame jfr;
int num = 0;
float z = 0f; //
Literale
InputDialog() {
jfr = new JFrame("Eingabedialog");
icon = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getImage("dh.png");
jfr.setIconImage(icon);
jfr.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
jfr.setSize(349, 301);
jfr.setResizable(false);
jfr.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
jfr.setVisible(true);
}
String showQuestionDialog(String txt) { //
Methoden
return JOptionPane.showInputDialog (
jfr,
txt
);
}
void showErrorDialog(String txt) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog (
jfr,
txt,
"Eingabefehler",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE
);
}
void show() {
String input;
while (true) { //
Kontrollstrukturen
try {
input =
showQuestionDialog("Eine ganze Zahl bitte:");
num = Integer.parseInt(input); //
Wrapper-Klassen
break;
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
showErrorDialog("Dies ist keine ganze Zahl!");
}
}
while (true) {
try {
input =
showQuestionDialog("Eine Zahl vom Typ \"float\" bitte:");
boolean b = input.endsWith("f")||input.endsWith("F");
if (!b) input = "x";
z = Float.parseFloat(input);
break;
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
showErrorDialog("Die Eingabe war nicht korrekt!");
}
}
System.exit(0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputDialog dialog = new InputDialog();
dialog.show();
}
}
